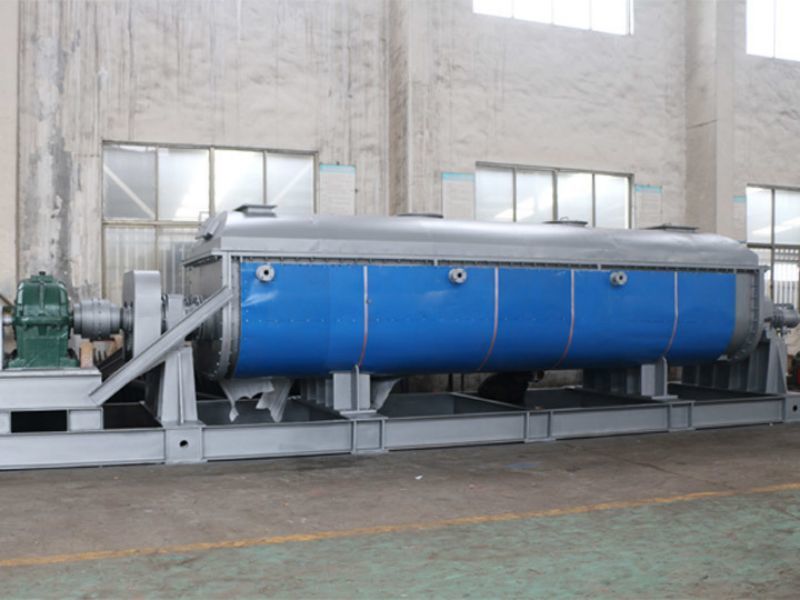
Overview of complete treatment technology and equipment for sludge drying and incineration
Category
Enquiry
Parameter download
Main types of sludge treated
Domestic sludge, chemical sludge, white sludge, oil sludge, textile sludge, pulp sludge, pigment sludge, electroplating sludge, etc.
Composition of sludge
Sludge is mainly composed of low-level organic compounds such as amino acids, humic acid, bacteria and their metabolites, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, heterocyclic compounds, organic sulfides, volatile odors, organic fluorides, etc. In addition, it also contains inorganic substances and heavy metal substances such as mercury, cadmium, and lead. Sludge is a by-product with a large volume generated from sewage treatment, generally with a moisture content of 80-90%. For every 10000 cubic meters of sewage treatment capacity, more than 10 tons of sludge can be produced (calculated based on sludge with a moisture content of 80-90%).
Main characteristics of sludge
The sludge generated by general sewage treatment plants is a solid or fluid substance with a moisture content ranging from 65% to 90%. The solid components are mainly composed of organic residues, bacterial cells, inorganic particles, colloids, and flocculants used. It is a complex mixture mainly composed of organic components, including potentially valuable organic matter, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and various trace elements.
(1) Physical characteristics
The composition of sludge is composed of suspended solids in water that are bound and condensed in different ways. The structure is loose, the shape is irregular, the specific surface area and porosity are extremely high (porosity is often greater than 99%), the water content is high, and the dewatering performance is poor. It has a fuzzy like branching and mesh structure in appearance.
(2) Chemical characteristics
Biological sludge is mainly composed of microorganisms, including solid particles such as sediment, fibers, animal and plant residues mixed with domestic sewage, as well as organic matter, metals, bacteria, insect eggs, and other substances that may be adsorbed. Sludge also contains nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium required for plant growth and development, as well as various trace elements that maintain normal plant growth and development, and organic matter that can improve soil structure.
(3) The forms and properties of water in sludge
There are four forms of water in sludge: surface adsorbed water, interstitial water, capillary bound water, and internal stagnant water. Capillary water is divided into fissure water, pore water, and wedge-shaped water. The water adsorbed by surface tension is called surface adsorbed water. Gap water generally accounts for 65% to 85% of the total water content in sludge, which is the main target of sludge concentration. Capillary bound water: Concentration cannot separate capillary bound water, and separating capillary bound water requires high mechanical forces and energy, such as vacuum filtration, pressure filtration, centrifugal separation, and extrusion to remove this part of water. Various types of capillary bound water account for about 15% to 25% of the total water content in sludge. Internal bound water: refers to the water contained within the microbial cells in the sludge, and its content is related to the proportion of microbial cells in the sludge. Removing this part of water requires breaking the cell membrane, causing the cell fluid to seep out and transform from internal bound water to external liquid. Internal bound water generally accounts for only about 10% of the total water content in sludge.
Difficulties in sludge treatment
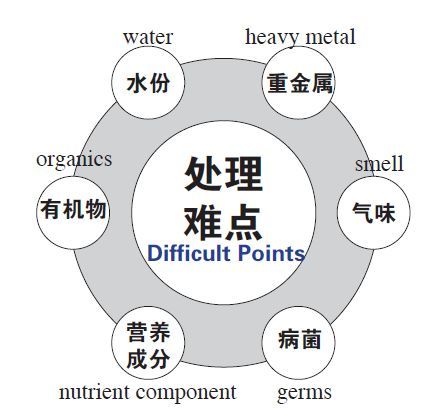
The goal of sludge treatment

Related Equipment
Leave your needs behind
We will contact you within one working day. Please pay attention to your email.



